ChatConnector
Configuration Methods
The configuration of ChatConnector is stored in an initialization (*.ini) file. Unless explicitly specified by a command line argument, the path to the ini-file is the name of the executable file with the exe extension replaced by “.ini”.
There are two ways to change the configuration of ChatConnector. Either by directly editing the configuration in the ini-file or by using the ChatConnector’s remote console. In both cases restarting the application might be required for the changes to take effect.
Direct Edit
To directly edit the ChatConnector’s configuration, open the ini-file, perform your changes and make sure that the syntax is correct (the ini-file is read by standard Win API functions and save it).
Configuration Sections
In the ini-file, configuration sections are declared by terms surrounded by square brackets. All subsequent key-value pairs are assumed to be inside this section.
Example
[Gate_mcil]
Multi-Valued Keys
Multivalued keys are suffixed with their contiguous zero-based index surrounded by brackets.
Example
Username(0)=chatsupport@bucher-suter.com
Password(0)=!7sad&ag*36
ScriptSelector(0)=BucherSuter_support
Remote Console Edit
You can start the remote console monitors via a Telnet session or by using a DOS command prompt. Please note that only local access is possible.
Telnet Client is not installed by default on Windows Server 2008 and higher. As the remote console process of the ChatConnector can only be accessed locally, it is required to install Telnet Client on each server where ChatConnector is deployed. If the client is installed a Telnet session can be started by entering the following command in a DOS command prompt:
C:\>telnet localhost <TelnetServerPort>
or directly in a Telnet session:
Welcome to Microsoft Telnet Client
Escape Character is 'CTRL+¨'
Microsoft Telnet> open localhost <TelnetServerPort>
localhost indicates a connection to the local server and is the same as the 127.0.0.1 IP address which always points to the local host.
\<TelnetServerPort> is the address of the ChatConnector’s local remote console port, which is set by the key TelnetServerPort in the
ChatConnector ini-file, default 9010
After the console is started the following prompt appears:
>
Configuration Command
Use the cfg command to access the configuration values.
Syntax
[@<gateid>] cfg [{<key> [<value>]} | !save]
<gateid> is the gate id to access the configuration. If this part is omitted, the core configuration is accessed. This parameter determines which of the top-level sections should be accessed.
<key> is the key to access. If the key value pair is not in a top-level section, the path is determined automatically. If this parameter is omitted, the remote console displays all the possible keys.
<value> is the value to set for a given key. If the value contains whitespaces, it must be surrounded with quotes. If the value contains quotes or backslashes, they must be escaped with a leading backslash. If this parameter is omitted, the current value is displayed.
After having modified some settings, do not forget to save the configuration using the “!save” syntax (this must be done separately for each part – core and gates).
Example
The following example...
- ...queries the current value for the key MmPortA in gate mcil
- ...sets the value for the key MmPortA in gate mcil to 7051
- ...sets the value for the key AutoStartHttpServer in the configuration section core to false
...and saves the changes.
>@mcil cfg MmPortA
7050
>@mcil cfg MmPort 7051
Value changed.
>cfg AutoStartHttpServer false
Value changes.
>@mcil cfg !save
Configuration saved
>cfg !save
Configuration saved.
Complex and Multivalued values
There is a special syntax to set the value of complex types or multivalued types, or a mixture of both. With this syntax, strings must be surrounded by quotes even if they do not contain whitespaces. The configuration of complex and multivalued types is decorated with explicit examples.
Set a list
This is achieved by separating the values by a comma and enclose all values in curly brackets.
{value0,value1,value2,…}
Set a structure
This is achieved by setting the fields using an equal sign and putting the field name on its left-hand side
and the field value on the right-hand side, separating the fields assignments by commas and enclose all values in curly brackets.
(key1=value1,key2=value2,…)
Example
This example creates a list of two chat users: alice with password 1234 and bob with password 5678.
\> @jabber cfg ChatUsers (username=\"alice\",password=\"1234\"),(username=\"bob\",password=\"5678\")
Notice the use of a leading backslash before every quote-character (escaping).
Core Configuration
| Key | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| AutoStartHttpServer | Defines whether to start the HTTP server automatically at startup. | Boolean | True, 1 |
| AutoStartTelnetServer | Defines whether to start the telnet server automatically at startup. | Boolean | True, 1 |
| ChatSessionHistoryMaxSize | The maximal number of messages saved in a chat session history. | Positive integer | 50 |
| HttpAllowedHosts | Define allowed client access. | Regular expression | 127\.[\d.]+|[0:]+1|localhost |
| HttpServerPort | The port to listen for HTTP connections (aka status page). | Positive Integer (5000 – 65535) | 9080 |
| LogFile | Log file path | String | \<System>:\\<ProgramData>\BucherSuter\logfiles\ChatConnector\McilChat_\<instance>.log |
| LogMask | Logging mask | 32 bit hex | 0x80000004 |
| MaxChatSessionLimit | Maximum of simultaneous chat sessions | Positive integer | 500 |
| MaxLogFileCount | Max number of preserved log files | Positive integer | 5 |
| MaxLogFileSize | Maximum size of a log file | String | 10MB |
| TelnetAllowedHosts | Define allowed client access | Regular expression | 127\.[\d.]+|[0:]+1|localhost |
| TelnetServerPort | The port to listen for telnet connections (aka remote console) | Port number | 9010 |
| UrlEncodeChatMessages | Enables URL encoded/decoded chat message to support special characters | Boolean | false |
Verify Core Configuration
If you connect to the ChatConnector’s HTTP server after having restarted the ChatConnector, you should see the ChatConnector status page with one main section labeled “Core” and one section for each gate labeled “Gate <gateid>”.
Special characters
In order to support UTF-8 Multibyte special characters (e.g. Hebrew), the ChatConnector uses URL-encoding/decoding. The ChatConnector URL-encodes a chat message and transfers it as ASCII-code through the ConnectMCAL and MediaManager components. This requires, that the CRM or the CRM connector as well as the chat client has to support URL-encoded/decoded chat messages to be able to decode the URL-encoded chat message.
To enable URL-encoded/decoded chat messages, following parameter has to be set into the [core] section of the config file of the ChatConnector:
[core]
UrlEncodeChatMessages=true
...
MediaManager-Gate Configuration
The configuration section in the ini-file is thus [Gate_mcil].
| Key | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| AllowedIdleTime | Max time for an idle chat session | Positive integer | 3600 |
| ApplicationId | MediaManager application identifier | Positive integer | 999 |
| ChatBeingFailoveredMessage(CBF) | Chat message sent when session was closed by failover. | String | The chat session is currently stopped by failover. Please be patient. |
| ChatBeingTransferredMessage(CBT) | Chat message sent during session transfer to another agent. | String | The chat session is being transferred to another agent. Please be patient. |
| ChatIdentifier | Private. Do not change this! | String | "chat://" |
| ChatPartnerFound(CPF) | Chat message sent after session transfer. | String | You are now connected with an agent. |
| ClearHistoryOnTransfer | Clear history buffer before transfer to second agent. If CRM provides its own transcript transfer to transfer target, Chat Conntector’s transcript buffer can be cleared by setting this to True. | bool | False (for Siebel set this value to True) |
| CustomerAccepted (CA) | Chat message sent to customer on connect. | String | “” |
| HeartbeatInterval | The amount of time between two heartbeats. This value must be less than the MediaManager’s \< HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT>. | Positive integer | 5000 |
| HistoryAgentPrefix | Prefix for messages replayed from message history buffer on agent selection. For default setting “NAME” peer remote name is used. | String | "NAME" |
| HistoryCustomerPrefix | Prefix for messages replayed from message history buffer on agent selection. If “HistoryAgentPrefix” is not “NAME” messages for agent are prefixed with this setting. | String | “(cust)” |
| InternalErrorMessage | Chat message sent when an internal error occurs. | String | Our servers are busy and your request could not be processed. We are sorry for the inconvenience. Please try again later. |
| LogMcilCommunications | Defines whether to log or not MCIL communications. | Boolean | True |
| LogMcilIgnoreHeartBeats | Defines whether to ignore MCIL heartbeats when logging MCIL communications. | Boolean | True |
| LookingForChatPartnerMessage | Chat message sent when system is looking for an available agent | We are currently looking for your chat partner. Please be patient. | |
| MaxRerouteCount | Shutdown of user session if value is reached | Positive integer | 10 |
| MmHostA | The media manager hostname | String | “localhost” |
| MmHostB | The media manager hostname | String | “” |
| MmPortA | The media manager port. | Port number | 7050 |
| MmPortB | The media manager port. | Port number | 7050 |
| RequestTimeout | The allowed amount of time in milliseconds to perform a request and receive the response. | Positive integer | 5000 |
| RunScriptParameterInName | Name of UCC variable for parameter transfer. Ex. ECC.user.BS_inout | String | “ECC.user.BS_inout” |
| RunScriptParameterOutName | Name of UCC variable for parameter transfer. Ex. ECC.user.BS_inout | String | “ECC.user.BS_inout” |
| SessionClosedByOverflow | Chat message sent when session was close by overflow. | String | The chat session is closed by overflow. |
| SessionClosedByReroute | String | This chat session was closed by the reroute. | |
| SessionClosedMessage | Chat message sent when chat session is closed. | String | This chat session is closed. |
| SystemMessagePrefix | Chat message prefix for messages issued by the system. | String | "\<SYSTEM> " |
| VarPool | Define your own Runscript variables. (see chapter 4.3, 8.2.4/8.2.5) | “” | |
| KVPTransferDelimiter | Key/Value pair delimiter to separate single pairs. See chapter 9.1 Passing Data to the ChatConnector for more information. | Char | “|” (pipe character) |
Application Identifier
First of all, you have to make sure that the ChatConnector’s application ID is unique amongst all the applications that connect to the MediaManager. If it is not, you must set ApplicationId to a different value.
Connection to MediaManager
You must specify the host and the port of the MediaManager. Set the values MmHostA, MmHostB and MmPortA, MmPortB. Verify the connection to the MediaManger by using the ChatConnector’s web status page.
VarPool
The ChatConnector’s Variable Pool (VarPool) feature allows the definition of “communication” variables (key/value pairs) which can be set and/or retrieved in a Cisco CCE routing script by using the RunScript-node and forwarded to b+s Siebel or SAP CRM Connectors (see also chapters Set Parameter and Get Parameter)
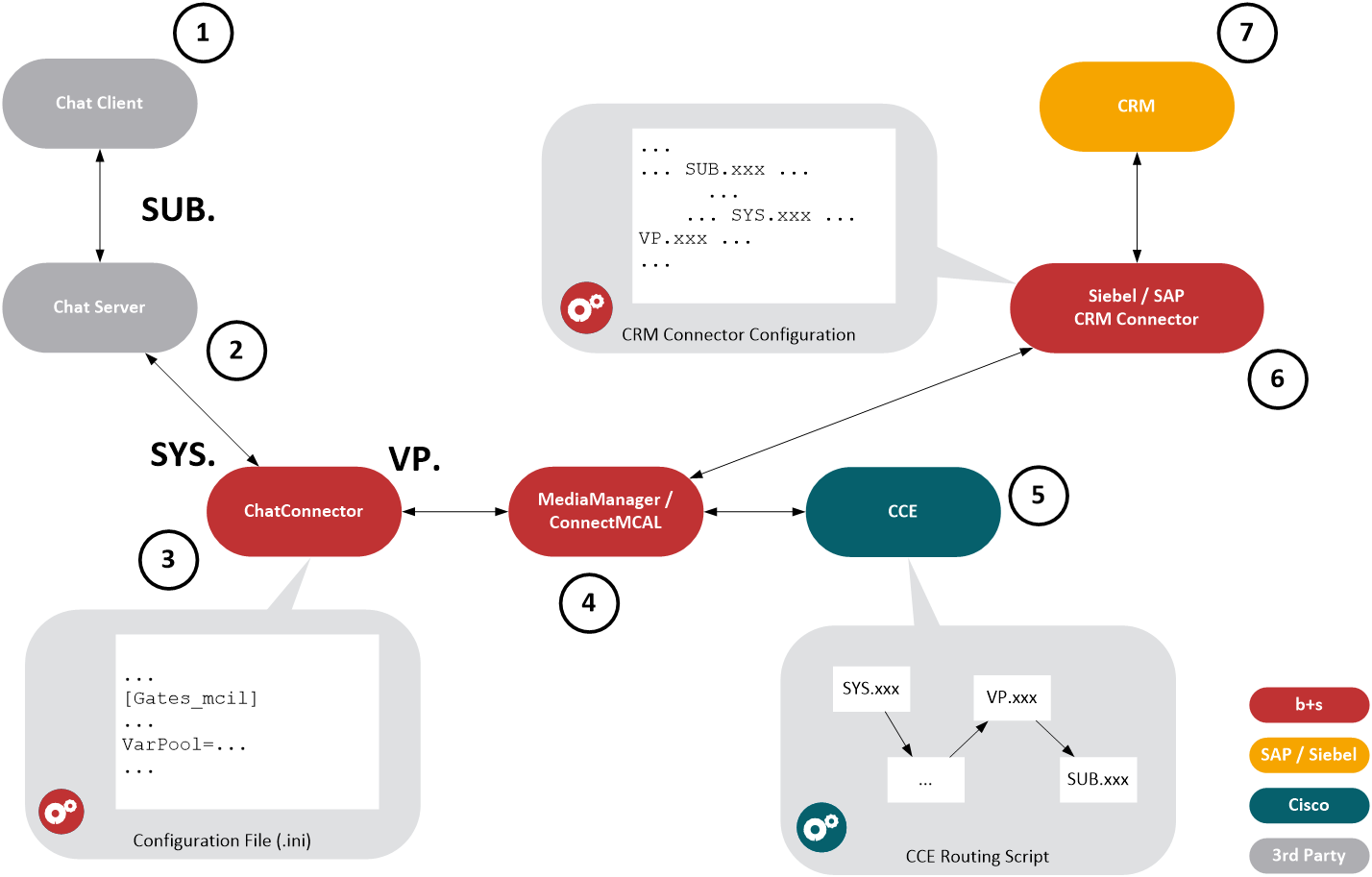
Marker 1: Chat Client
- A (web) chat client can provide a set of variables (key/value pairs). They are sent to the ChatConnector in the first XMPP
message stanza either using the child element
subjectorbody(see chapter Transmitting Customer Data to CCE for further information)- It might be desired that certain data about the customer and/or the customer’s intention is passed from the end user chat client via the chat server and the ChatConnector to CCE or to the agent itself. Having such data available in CCE makes it possible to refine the agent selection process in the CCE routing script.
- These set of variables are prefixed with
SUB.
Marker 2: Chat Server
- The chat server connects the chat client and the ChatConnector with each other.
Marker 3: Chat Connector
The ChatConnector knows two other categories of communication variables beside the ones prefixed with
SUB:SYSandVP.The first category of variables is defined by the ChatConnector itself. These variables are prefixed with
SYS.The second category of variables can be defined by an administrator in the ChatConnector’s ini-file, configuration section [Gates_mcil], parameter name VarPool. These variables are prefixed with
VP.Format of the configuration parameter:
VarPool=Key{=”Value”[Flags]};Key ...where the part in curly brackets is optional. Default flag isRWMeaning of the flags (simple access control):
Name Meaning R Variable can be read by using Get Parameter W Variable can be set by using Set Parameter T Variable is transferred to MediaManager and a subsequent OFFER_TASK_EVENT transfers it to the b+s Siebel or SAP CRM Connector respectively to the CRM agent. SUB. –variables, transported from the customer’s chat client to the ChatConnector, can be predefined in the ChatConnector’s VarPool-parameter to get other access rights (read access is default).
Configuration Example:
VarPool=Nickname[RWT];SUB.SRNumber[RT]Defines two variables:
Nicknamewith read & write access and transfer capability to the agent and a predefinition ofSUB.SRNumberwhich can only be read and is also transferred to the agent.The state of VarPool variables can be queried by using the ChatConnector’s remote console command
$mcil vp <username>
Marker 4: MediaManager / ConnectMCAL
- MediaManager and ConnectMCAL transfer the received VarPool-variables to CCE respectively to the Siebel or SAP CRM Connector.
- Check the b+s MCA for SAP or b+s MCA for Siebel product documentation for required configuration settings of the MediaManager or ConnectorMCAL to use the VarPool-feature
Marker 5: CCE
- See chapter Module Scripting in CCE for getting and setting VarPool-variables from the CCE routing script.
Marker 6 and 7: Siebel / SAP CRM Connector, Siebel / SAP CRM
- As previously mentioned, variables flagged with T are transported to the b+s Siebel or SAP CRM Connector in an OFFER_TASK_EVENT by the MediaManager. This allows Siebel administrators to use this kind of variable directly inside Siebel configuration (i.e. Siebel Definition Files and ‘Communication’ settings).
Jabber-Gate Configuration
The configuration section in the ini-file is thus [Gate_jabber].
| Key | Description | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatSessionRemove DelayInSeconds | If XMPP presence notifications are available (depends on the chat server and group settings), chat sessions are disposed after this period of time. | Integer | 10 |
| Compress | XMPP communication compression | bool | False |
| Encrypt | XMPP communication encryption (TLS) | bool | True |
| JabberServerHostname | Hostname of the chat server | String | 127.0.0.1 |
| JabberServerPort | Port of the chat server | Positive Integer (5000 – 65535) | 5222 |
| LogChatMessages | Write content of chat messages into the ChatConnector’s log file | bool | False |
| ReconnectTimeout | Time in milliseconds that must elapse between connection attempts. | Integer | 5000 |
| Chatstates | Transfer of ‘Composing’ chat state to agent client and vice versa. | bool | False |
Connection to Chat Server
You must specify the host and the port of the Jabber server. Set the values JabberServerHostName and JabberServerPort.
You must specify the host and the port of the chat server. Set the values JabberServerHostName and JabberServerPort. Verify the connection to the chat server by using the ChatConnector’s web status page.
Chat Users
The ChatConnector’s chat users can be defined in configuration section [DnChatUsers]. The username of a chat user must be unique. Furthermore, a Cisco CCE Script Selector must be associated with each user. Remember that the configured chat users must also be configured in the connected chat server.
| Key | Default | Range | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Username(n) | <empty> | - | username, must be unique across all gates |
| Password(n) | <empty> | - | password of the corresponding user (see chapter Encryption of Chat User Passwords) |
| ScriptSelector(n) | <empty> | - | CCE/CCH Dialed Number / ScriptSelector of corresponding user |
Example
In this example two chat users are created:
| Purpose | Username | Dialed Number / ScriptSelector |
|---|---|---|
| A service than can be contacted for technical support | chatsupport@bucher-suter.com | BucherSuter_support |
| A service that can be contacted for sales information | chatsales@bucher-suter.com | BucherSuter_sales |
Using Direct Edit:
[DnChatUsers]
Username(0)=chatsupport@bucher-suter.com
Password(0)=Zk4332sed
ScriptSelector(0)=BucherSuter_support
Username(1)=chatsales@bucher-suter.com
Password(1)=aF9656opa
ScriptSelector(1)=BucherSuter_sales
Encryption of Chat User Passwords
The passwords for the “DnChatUsers” can be stored in plaintext in the ChatConnector’s .ini file. To encrypt the passwords use the IniFilePasswordEncryptor.exe tool which is copied into the installation directory of the ChatConnector during the installation process.